Introduction to Vitamin D3 and Its Impact on All Over Body
Vitamin D3, crucial for bone mineralization, cell growth regulation, and immune system and neuromuscular functions, also plays a pivotal role in hormonal balance, impacting health issues such as infertility.
Resourced Information. The Role of Vitamin D in Hormonal Balance
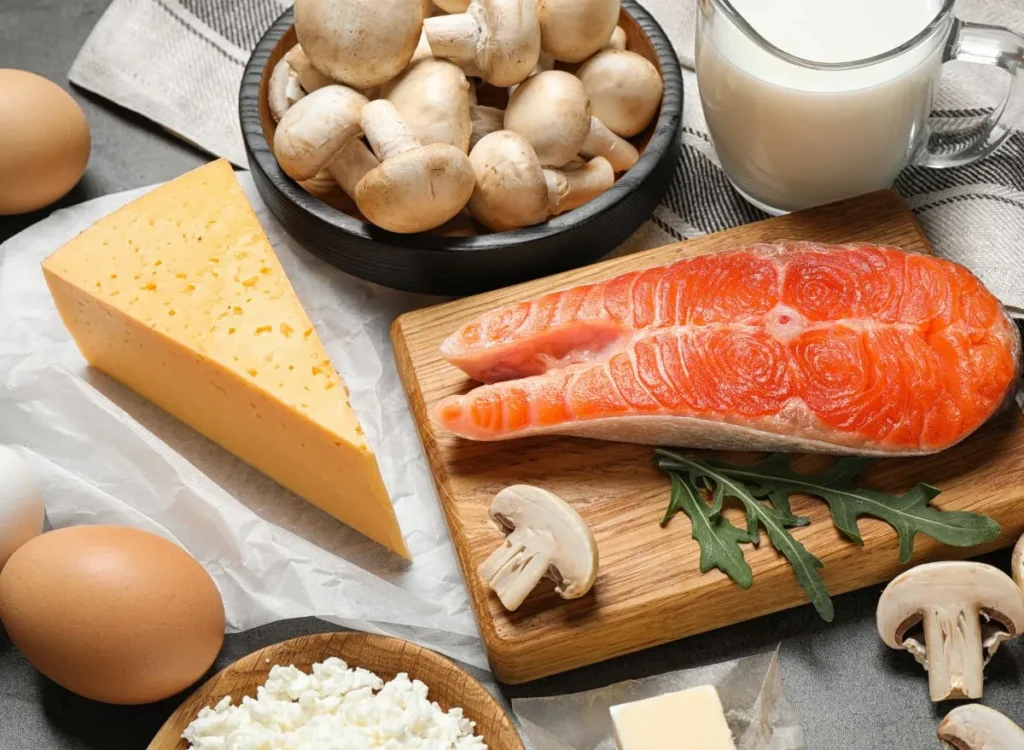

Vitamin D can be obtained through various sources. The primary natural source is sunlight, which triggers vitamin D synthesis in the skin when ultraviolet B (UVB) rays interact with a cholesterol derivative. Dietary sources of vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and tuna), egg yolks, and fortified foods like milk, cereal, and orange juice. Supplements are another reliable source, especially in regions with limited sunlight exposure or for individuals with dietary restrictions. The body’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight and absorb it from foods underscores the importance of maintaining adequate intake to support bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.
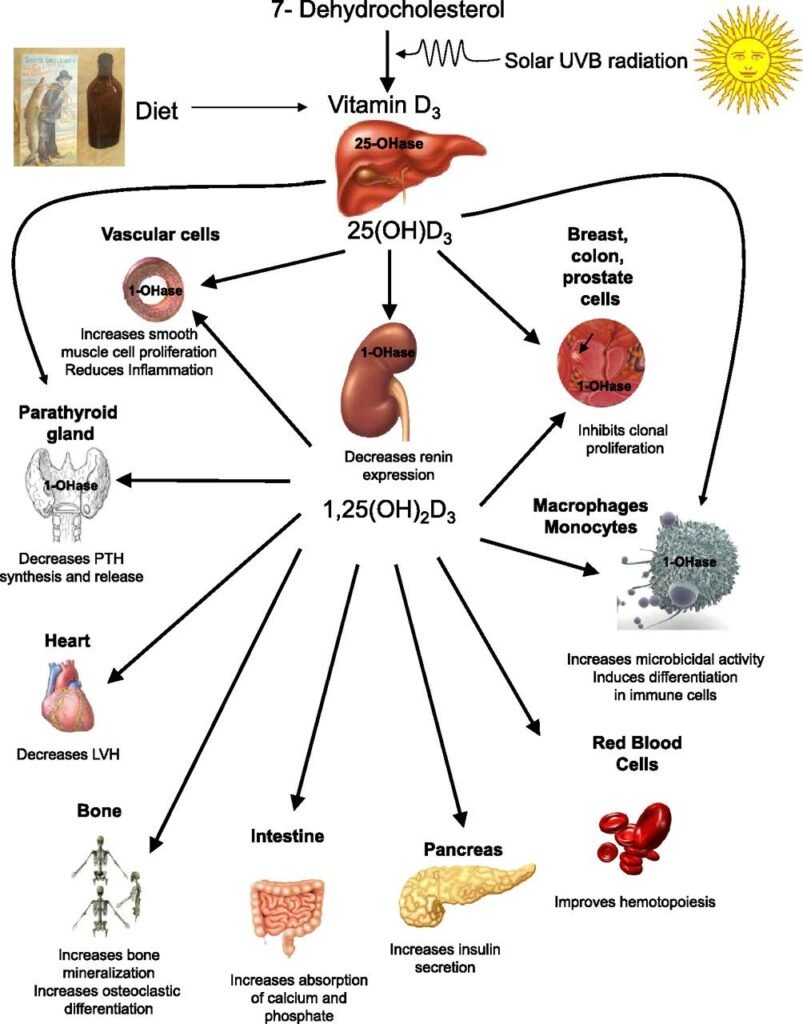
In humans, vitamin D synthesis begins when sunlight triggers the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin to vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). This compound is then metabolized into 25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcidiol) in the liver. The active form, calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3), is synthesized in the kidneys, with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels serving as a measure of vitamin D status.
Beyond its crucial role in calcium-phosphate metabolism, vitamin D enhances calcium absorption in the intestine, reabsorption in the kidneys, and bone formation through pathways such as the RANK/RANKL pathway in osteoclasts.
Vitamin D interacts with thyroid hormones and parathyroid hormone (PTH), influencing calcium levels and bone health. Studies indicate associations between vitamin D deficiency and autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, suggesting potential therapeutic benefits of vitamin D supplementation.

Additionally, vitamin D modulates immune cell activity by regulating cytokine production, potentially impacting conditions such as thyroid cancer positively.
In males, vitamin D levels correlate with steroid hormone production and sperm maturation, potentially affecting male fertility. Research links vitamin D deficiency with lower testosterone levels, highlighting its role in male reproductive health.
For females, vitamin D influences estrogen and progesterone levels, impacting menstrual regularity, fertility, and pregnancy outcomes. Deficiency has been associated with conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), affecting insulin secretion and resistance.
Studies underscore the importance of vitamin D in reproductive health and suggest potential benefits of supplementation in improving fertility and managing hormone-related disorders.

Research has identified vitamin D receptors (VDR) and 1α-hydroxylase expression in immune cells, including T and B lymphocytes, monocytes, dendritic cells, and neutrophils, suggesting a role in immune modulation. Vitamin D enhances the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-4, IL-5, IL-10) while inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, IL-12, IFN-γ, TNF-α), which may contribute to its potential therapeutic effects in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions.
Drostanolone Propionate: The Game-Changing Elixir in Bodybuilding
In conclusion, vitamin D’s multifaceted roles in hormonal balance and reproductive health underscore its significance beyond bone health. While sunlight remains a primary source of vitamin D, dietary sources and supplements play crucial roles in maintaining adequate levels, particularly in regions with limited sunlight exposure. Future research should continue exploring vitamin D’s therapeutic potential in managing various health conditions, including infertility, autoimmune diseases, and hormonal disorders.
Understanding the mechanisms by which vitamin D influences hormone synthesis and immune function provides insights into its broader implications for health and disease prevention. As researchers delve deeper into these interactions, optimizing vitamin D levels through supplementation and lifestyle adjustments may offer promising avenues for improving overall health outcomes.