Avian Influenza Unveiling the Threat Beyond the Feathers
Introduction
Avian influenza, often referred to as bird flu, is a viral disease that has garnered global attention for its potential to cause widespread health and economic crises. While much has been written about this infectious ailment, this article aims to delve deeper into the various facets of avian influenza, providing a fresh perspective on its causes, consequences, and prevention measures.
Understanding Avian Influenza

Avian influenza is a contagious viral infection primarily affecting birds. While birds are the natural hosts, certain strains have the capacity to infect other animals, including humans. This zoonotic potential is what makes avian influenza a topic of concern.
Types of Avian Influenza
Avian influenza viruses are categorized based on their surface proteins: hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N). There are numerous subtypes of avian influenza viruses, with H5N1 and H7N9 being some of the most well-known. While some strains cause mild illness in birds, others can lead to severe disease and high mortality rates.
Transmission and Spread
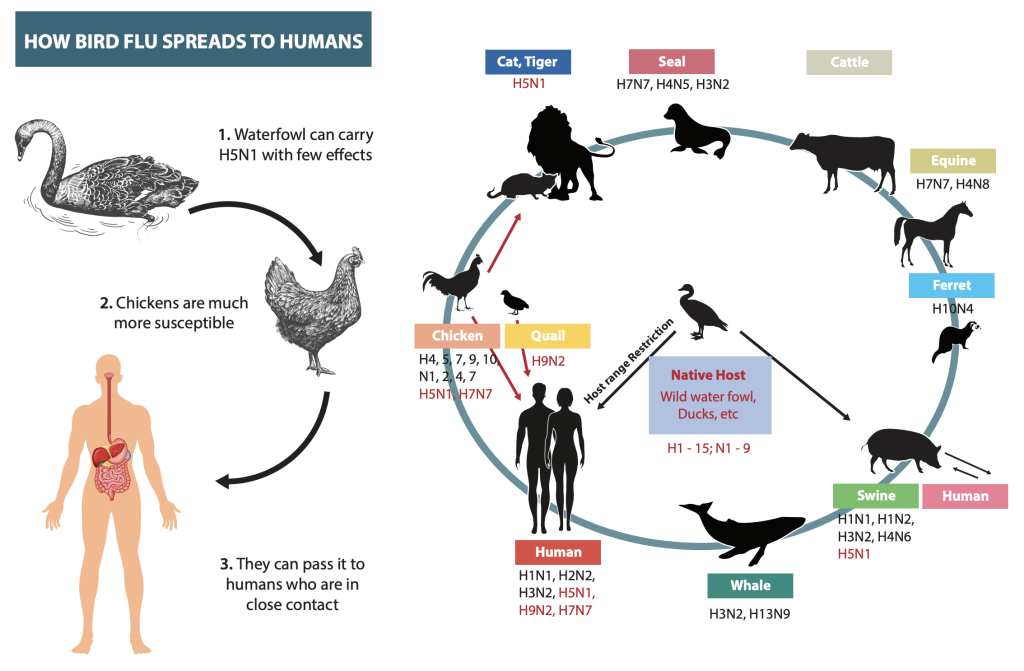
The transmission of avian influenza among birds occurs through contact with infected birds, contaminated environments, or ingestion of contaminated water or feed. Wild birds are often natural carriers and can spread the virus during migration. Infections can also occur in domestic poultry farms.
Human Transmission
Human transmission is rare but can happen, particularly in cases of close contact with infected birds. The consequences can be severe, leading to respiratory distress and, in some cases, death. The possibility of human-to-human transmission is a critical concern, as it could lead to a widespread pandemic.
Economic Impact
Avian influenza outbreaks can have a devastating economic impact. Infected birds in commercial poultry farms often necessitate mass culling, leading to significant financial losses. Trade restrictions on poultry products can further exacerbate these losses.
Global Concerns
Avian influenza is not limited by geographical boundaries. The interconnectedness of the modern world makes it a global concern. Rapid international travel and trade mean that a local outbreak can quickly become a transcontinental issue.
Recent Outbreaks
Several regions have witnessed avian influenza outbreaks in recent years. The H5N1 strain, in particular, has caused concern. East and Southeast Asia have been heavily affected by outbreaks, but the virus has also been reported in other parts of the world, including Europe.
Prevention and Control
The prevention of avian influenza requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Biosecurity Measures: Proper biosecurity measures in poultry farms can prevent the introduction and spread of the virus. This includes restricting access to farms, disinfecting equipment, and practicing strict hygiene.
- Vaccination: Vaccination of poultry is an essential tool in controlling avian influenza. Developing effective vaccines is an ongoing effort.
- Surveillance: Monitoring and surveillance programs help detect the virus early, allowing for prompt action.
- Risk Communication: Effective risk communication to the public, poultry workers, and stakeholders is vital to ensure a coordinated response.
- Antiviral Medications: Antiviral medications can be used as a preventive measure in some cases.
- International Cooperation: Global cooperation and information sharing are essential for preventing and responding to avian influenza outbreaks.
- click here for more latest articles
Challenges and Controversies
The prevention and control of avian influenza are not without challenges and controversies:
- Culling of Infected Birds: The mass culling of infected birds is a contentious issue, as it leads to ethical concerns and economic losses.
- Zoonotic Potential: The zoonotic nature of avian influenza is a significant concern, as it could potentially lead to a global pandemic.
- Vaccination Strategies: Developing effective vaccines for avian influenza is an ongoing challenge, as the virus mutates frequently.
- Balancing Health and Economic Interests: Finding the right balance between protecting public health and minimizing economic losses in the poultry industry is a delicate task.
The Role of Research
Research plays a crucial role in understanding, preventing, and controlling avian influenza. Ongoing studies are focused on virus evolution, vaccine development, and antiviral medications. Researchers are also exploring the possibility of creating more sustainable and ethical methods of managing outbreaks.
Conclusion
“Avian influenza, known as ‘bird flu,’ is a global concern affecting animal populations, livelihoods, and human health. International organizations like the FAO, WHO, and WOAH promote collaborative efforts to safeguard animals and people. While primarily confined to birds, the virus poses potential risks for human transmission and emergence in mammals.
The H5N1 avian influenza, originating in 1996, continues to devastate birds and poultry across Africa, Asia, and Europe, with a variant (H5 clade 2.3.4.4b) extending to North and South America. In 2022, 67 countries reported outbreaks, causing significant poultry losses. With 14 more countries affected in 2023, vigilance is critical to prevent and control avian influenza.”
