Lead Poisoning Understanding and Unmasking the Silent Threat

Lead poisoning, often termed a “silent epidemic,” is a pervasive and enduring public health issue that warrants unwavering attention. This article delves into the depths of lead poisoning, elucidating its causes, effects, and innovative measures to prevent and combat this insidious threat.
What is lead poisoning
Lead poisoning, medically known as plumbism, is the result of the accumulation of lead in the body. Lead, a heavy metal, is toxic to the human body, and exposure to even small amounts can have severe health implications.

Sources of Lead Exposure
Lead is ubiquitous in our environment and can infiltrate various facets of daily life.

- Lead-Based Paint: Homes built before 1978 often contain lead-based paint. Deteriorating lead paint can create lead dust and chips, posing a risk, especially in older homes.
- Lead in Drinking Water: Aging plumbing and pipes, particularly in older homes, can leach lead into tap water.
- Soil Contamination: Soil can become contaminated with lead, often from lead-based paint and leaded gasoline. Children can ingest lead through soil contact or consumption.
- Occupational Exposure: Certain jobs, such as construction, painting, and battery manufacturing, can lead to occupational exposure.
- Imported Goods: Imported goods, such as toys, cosmetics, and ceramics, can contain lead. Lead exposure may occur through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact.
Lead Poisoning Lethal Effects
Lead poisoning can have devastating consequences, particularly on children and pregnant women
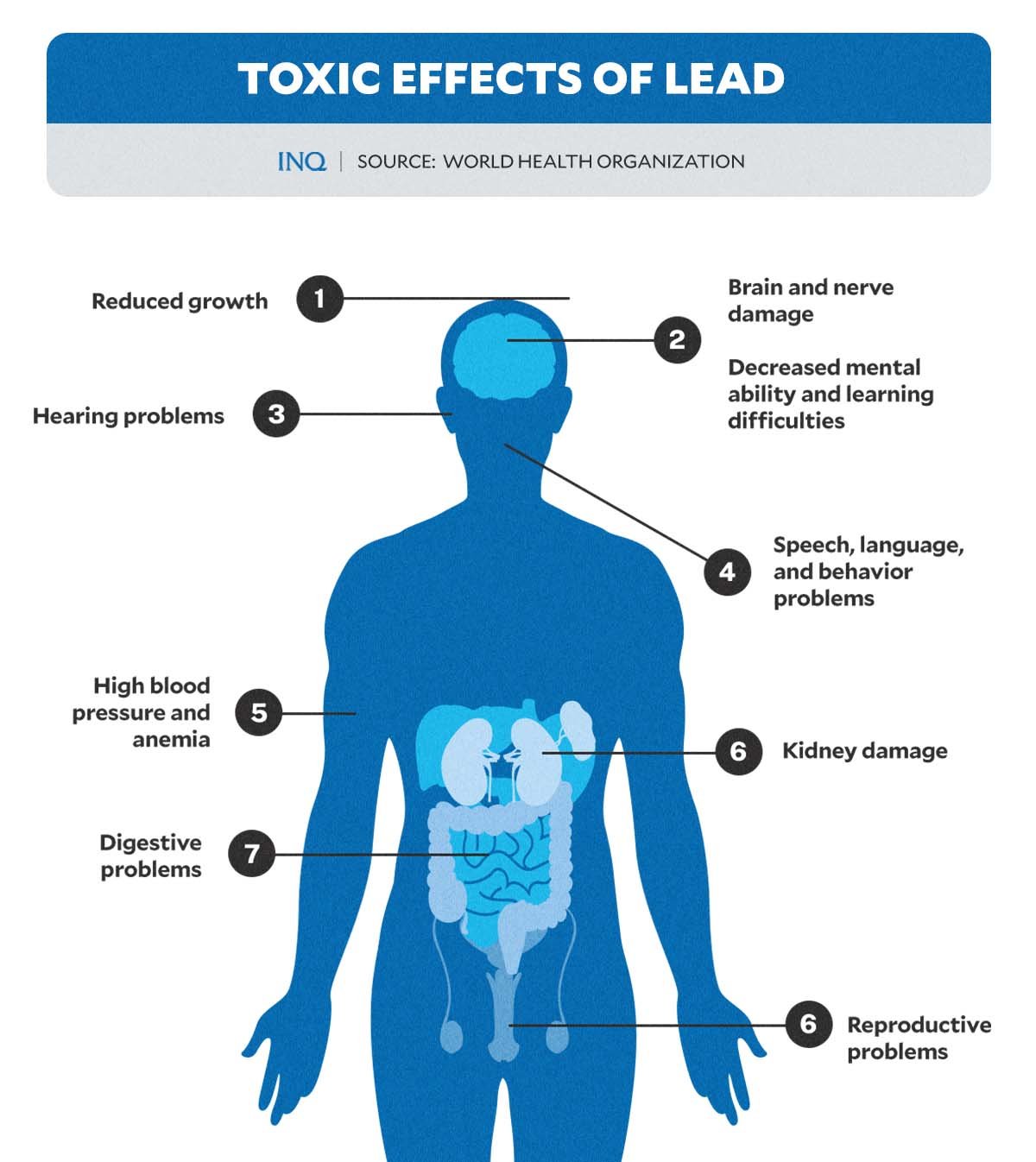
- Neurological Effects: Lead primarily affects the nervous system, causing cognitive and developmental impairments in children. It can lead to learning disabilities, reduced IQ, and behavioral issues.
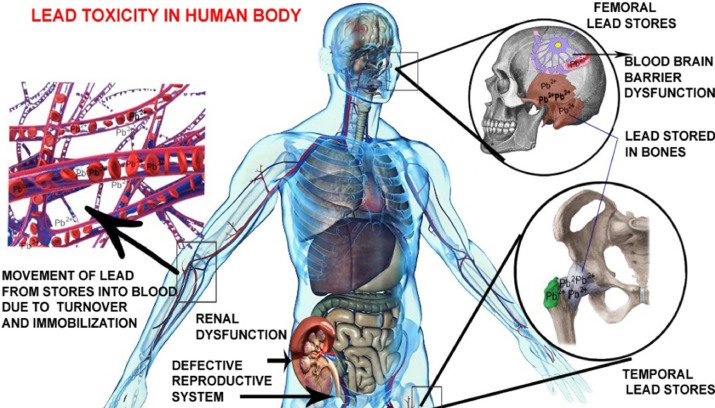
- Physical Health Implications: Lead poisoning can harm various organs, leading to anemia, kidney dysfunction, and hypertension in adults.
- Pregnancy Complications: Lead exposure during pregnancy can result in low birth weight, premature birth, and developmental delays in the child.
- Behavioral and Social Impact: The cognitive and behavioral issues associated with lead poisoning can impact an individual’s social life and opportunities.
Preventing Lead Poisoning A Multifaceted Approach
Preventing lead poisoning requires a comprehensive strategy that involves public policy, individual actions, and community efforts.
Safeguarding children from lead exposure is crucial for ensuring lifelong health. No safe blood lead level has been identified for children, as even low levels have been linked to adverse effects on learning, attention, and academic performance. Although the consequences of lead exposure may be lasting, early detection enables parents to take measures to prevent further exposure and mitigate damage to their child’s health.
RELATED ARTICLE Lead Poisoning Prevention
The primary and most effective strategy for preventing lead exposure is the removal of lead hazards from the environment before a child comes into contact with them. This proactive approach is key to ensuring that children do not suffer long-term harm from lead exposure. Additionally, secondary prevention involves measures such as blood lead testing and follow-up care, serving as a crucial safety net for children who may have already been exposed to lead.
A blood test is the most accurate means of determining lead exposure, measured in micrograms of lead per deciliter of blood (μg/dL). Despite the absence of obvious symptoms in most children with lead in their blood, discussing a blood lead test with the child’s healthcare provider is essential.

Notably, preventing childhood lead exposure is a cost-effective endeavor. An analysis by the Health Impact Project indicates that eliminating lead hazards from children’s living, learning, and playing environments could yield approximately $84 billion in long-term benefits per birth cohort. This approach not only benefits the current generation but also contributes to the well-being of future birth cohorts, with increasing savings over time. CDC is dedicated to addressing this threat and enhancing health outcomes for our nation’s most vulnerable citizens—our children
1. Removal of Lead-Based Paint
In older homes, the removal of lead-based paint and proper maintenance is crucial. Initiatives promoting the safe removal and renovation of such homes are essential.
2. Regular Testing of Drinking Water
Regular testing of drinking water is vital, especially in areas with older infrastructure. Filters and water treatment methods can be used to reduce lead content.

3. Lead-Safe Renovation
When renovating homes, employing lead-safe practices and hiring certified professionals can mitigate exposure risks.
4. Soil Testing and Gardening Safety
Testing soil for lead levels and adopting safe gardening practices can protect against soil-related exposure.

5. Occupational Safety Measures
Employers must implement safety measures for employees exposed to lead in the workplace, including appropriate personal protective equipment and education.
6. Consumer Awareness
Consumers should be informed about lead content in imported goods, cosmetics, and toys. Vigilance in product choices can minimize exposure risks.
7. Community Engagement
Engaging communities in lead poisoning prevention initiatives and educational programs can foster collective action and awareness.
Innovations in Lead Poisoning Prevention
Advancements in technology and awareness are driving innovative approaches to lead poisoning prevention:
1. Point-of-Use Filters
Technological innovations have led to the development of cost-effective point-of-use filters that can effectively remove lead from drinking water.
2. Mobile Apps
Mobile apps and websites offer resources for individuals to check lead levels in their neighborhoods, making information more accessible.
3. Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns, both online and offline, are being used to spread awareness and promote lead poisoning prevention practices.
4. Safe Play Areas
Communities are investing in lead-safe play areas for children, reducing the risk of exposure through contact with contaminated soil.
5. Lead-Safe Schools
Schools are adopting lead-safe practices, from drinking water testing to renovating lead-affected areas.
READ RESEARCHED ARTICLES Oral Sex & Throat Cancer Rising Rates of Public Health Concerns
Conclusion
Lead poisoning remains a significant public health concern, but with awareness, education, and collaborative efforts, it is a preventable issue. By taking proactive measures, individuals, communities, and governments can work together to eliminate the silent threat of lead poisoning, safeguarding the health and future of our most vulnerable populations. It’s time to unmask the silent threat and put an end to lead poisoning once and for all.