The Growing Concern of Leishmaniasis an Spreading Parasitic Disease in the United States
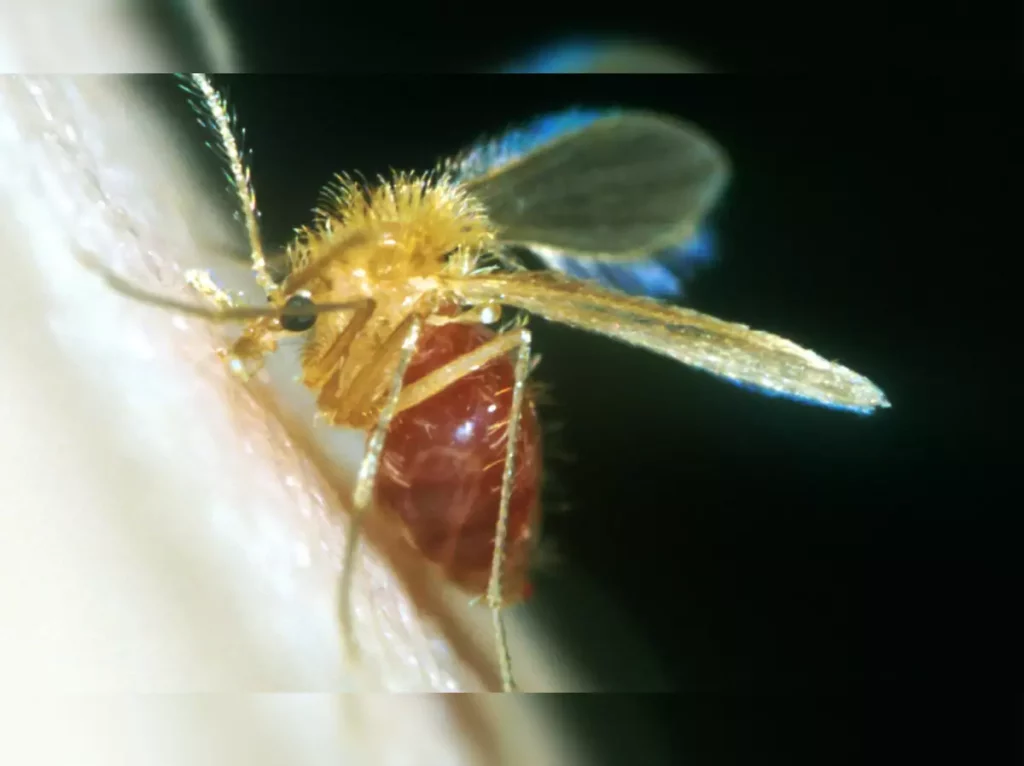
A new strain of a parasitic disease transmitted by flies has been discovered in the southern states of the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This disease, known as, is primarily spread through the bites of infected sandflies, leading to the development of skin sores in affected individuals within a few weeks of being bitten. While these sores often heal on their own, they can leave behind scars and disfigurement.
Leishmaniasis Overview
Leishmaniasis is a group of parasitic diseases caused by protozoa of the genus Leishmania. It can manifest in several forms, including cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral, each with varying symptoms and severity. The primary mode of transmission is through the bite of infected female sandflies.

Global Distribution
Leishmaniasis is prevalent in many parts of the world, with the highest number of cases reported in countries such as India, Sudan, Brazil, and Afghanistan. It affects both humans and animals, making it a zoonotic disease.
In the past, the CDC had attributed most cases of leishmaniasis in the United States to individuals who had traveled to or lived in tropical and subtropical countries, as well as southern Europe, where the disease is more commonly contracted. However, recent findings have raised concerns. In a new analysis, the CDC reported that they had identified 1,222 positive cases of leishmania in US citizens between 2005 and 2019. The majority of these cases were found in Texas, although they were not exclusive to the state. “Anecdotal” reports of locally-contracted leishmaniasis have also emerged from Florida, Oklahoma, and Arizona.
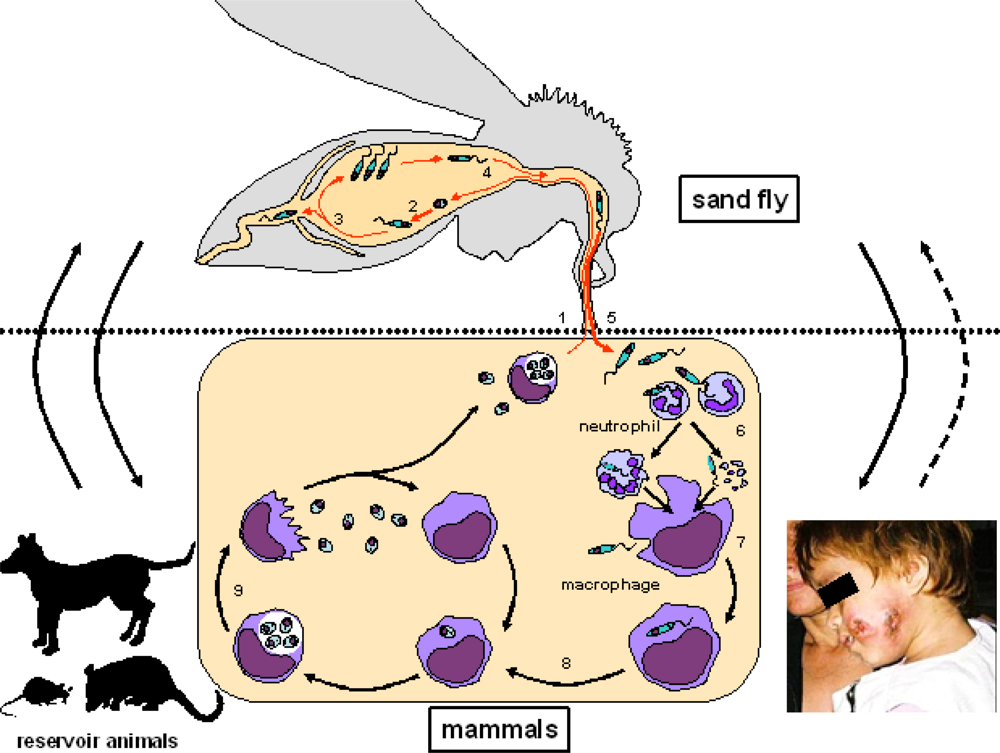
Symptoms and Complications: Cutaneous leishmaniasis typically causes skin sores, while mucocutaneous leishmaniasis can lead to severe facial disfigurement. Visceral leishmaniasis, the most severe form, can affect internal organs and can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosis often involves clinical evaluation, microscopic examination of tissue samples, or serological tests. Treatment includes antiparasitic drugs, but the choice of medication and duration of treatment may vary depending on the form of leishmaniasis.
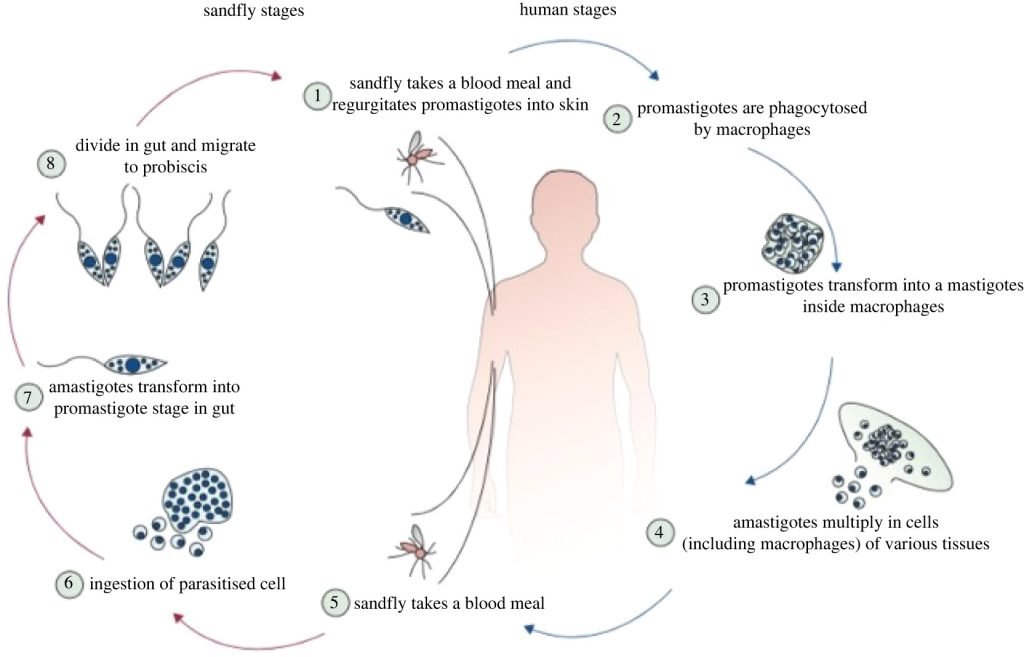
Prevention: Prevention methods include using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and using bed nets to avoid sandfly bites. Efforts to control sandfly populations through insecticide spraying have been employed in endemic areas.
READ MORE INTERESTING ARTICLES Oral Sex & Throat Cancer Rising Rates of Public Health Concerns
The CDC’s new findings suggest that 86 of the recent cases they have identified were found in people with no recent history of traveling outside of the US. These findings were presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene in Chicago, indicating that these cases may originate from a unique strain native to the US, genetically different from travel-related cases.
Public Health Significance
While leishmaniasis is not widespread in the United States, the recent discovery of locally-contracted cases in certain regions has raised awareness among public health professionals. This serves as a reminder that infectious diseases can adapt and spread to new areas, emphasizing the importance of surveillance and monitoring.
One Health Approach
Leishmaniasis highlights the One Health concept, recognizing the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, veterinarians, entomologists, and public health officials are essential to address the disease comprehensively.
Challenges in Disease Control
The lack of awareness about leishmaniasis, limited resources in endemic regions, and issues related to access to healthcare hinder effective control and treatment.
Future Prospects
Public health agencies like the CDC continue to monitor and investigate the disease to better understand its presence and potential risks in the United States. Awareness campaigns and training for healthcare professionals are vital to ensure early diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis.
In conclusion, leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease with different forms and impacts on public health. The recent emergence of cases in the United States, particularly in southern states, raises questions about its presence and potential risks in the country. While it may not pose a severe public health risk, awareness, surveillance, and collaborative efforts are essential to ensure timely diagnosis and effective management
1 Comment