Introduction Alzheimer And Its Cure
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a complex neurological condition that has eluded a cure for decades. Recent studies have shed light on novel insights into the cellular changes associated with early Alzheimer’s, providing hope for improved treatments. Additionally, the development of promising drugs offers fresh optimism for individuals living with Alzheimer’s and their families.

Recent research has unveiled a series of cellular changes that are unique to the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. These changes, previously unobserved in animal studies, offer valuable insights into the multifaceted nature of AD pathology.
RELATED ARTICLE Three promising drugs for treating Alzheimer’s disease bring fresh hope
Alzheimer’s, a multifaceted condition: Professor Fang Yu, from the Edson College of Nursing and Health Innovation at Arizona State University, highlights that Alzheimer’s disease involves various abnormal processes. These processes include neuroinflammation mediated by glia and astrocytes, which have gained increasing recognition.
Section 2: Groundbreaking Research on Live Human Brain Tissue
Traditionally, AD studies have relied on post-mortem autopsy samples for insights into the disease’s pathology. However, researchers have recognized the limitations of studying brain tissue after death. Neurons and other cells undergo rapid changes following deprivation of oxygen, making it challenging to pinpoint the earliest events that trigger plaque buildup and neuronal death.

Studying Live Human Brain Tissue: To address this limitation, a team led by the Broad Institute of Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard examined data from 52 living patients. They collected rare brain tissue samples from individuals at varying stages of AD-related changes, including those who were later clinically diagnosed with Alzheimer’s.

Observations from live human brain tissue: The study identified a set of cellular changes unique to the early stages of Alzheimer’s, providing a clearer understanding of the disease’s progression. These insights are essential for designing treatments that are most effective when initiated early.
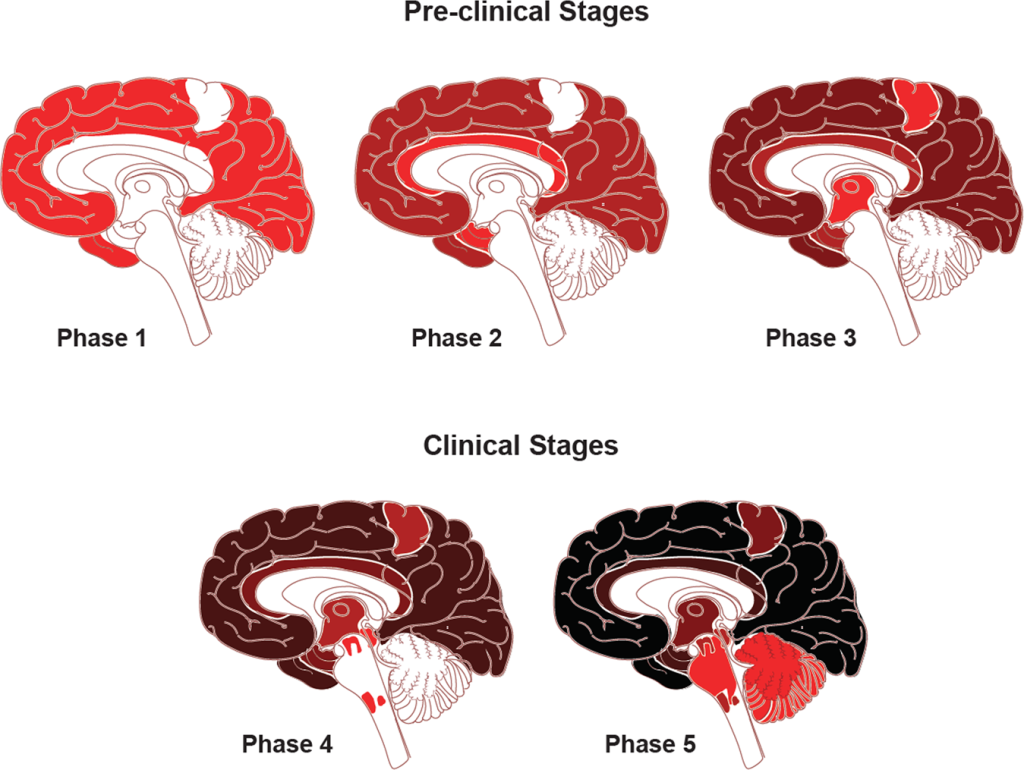
Section 3: Key Findings and Implications
Key findings from this research included the identification of a specific group of overactive neurons in the upper layers of the brain, which die early in AD. This hyperactivity is associated with gene expression signatures linked to amyloid production, a long-standing hypothesis in Alzheimer’s research.
New insights into plaque growth: By recognizing these hyperactive neurons’ role in amyloid production and observing similar signatures in oligodendrocytes, researchers have a potential target for Alzheimer’s drugs. Understanding how these cells stimulate plaque growth is a critical step towards identifying new drug targets.

Section 4: Promising Alzheimer’s Drugs
In addition to the groundbreaking research on cellular changes, there are promising drugs in development for Alzheimer’s disease. These drugs aim to slow down or even halt the disease’s progression, providing hope for patients and their families.
1. Donanemab A Breakthrough in Slowing Alzheimer’s Progression
Donanemab is an immunotherapy drug developed by Eli Lilly, administered via an intravenous drip. Clinical trials have shown its effectiveness in removing amyloid from the brain, slowing memory and cognitive decline by more than 20%. Importantly, earlier administration appears to yield greater benefits.
2. Lecanemab: A Game-Changer for Early Alzheimer’s Treatment
Lecanemab, marketed as Leqembi, is another immunotherapy drug developed by Eisai. It has been approved for early Alzheimer’s in the USA and is awaiting approval in the UK. Clinical trials indicate that it effectively removes amyloid and tau proteins, slowing cognitive decline by 27% and improving the quality of life.
READ RELATED ARTCLE Lecanemab Approved for Treatment of Early Alzheimer’s Disease

3. Remternetug: The Next-Generation Immunotherapy
Remternetug, also developed by Eli Lilly, represents a second-generation immunotherapy drug. It is currently being tested in phase 3 trials. Early data suggests that it may be more effective at clearing amyloid compared to donanemab. Remternetug’s method of subcutaneous injection aims to enhance effectiveness and reduce adverse effects.
RELATED ARTICLE Remternetug by Eli Lilly and Co for Alzheimer’s Disease: Likelihood of Approval
Section 5: The Road Ahead
The research and drug development in Alzheimer’s hold the promise of improved treatments and a brighter future for those affected by the disease. Researchers aim to identify proteins associated with cellular states as potential biomarkers for disease progression monitoring.

Collaboration and future insights: The collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies is crucial in advancing our understanding of Alzheimer’s. By sharing data and insights, the pathogenic process of Alzheimer’s and other brain diseases can be better understood.
Section 6: Challenges in Alzheimer’s Research
While there have been significant breakthroughs, Alzheimer’s research still faces several challenges. These challenges include funding, ethical concerns, and the need for further clinical trials.
1. Funding and Resources: Alzheimer’s research requires substantial funding and resources to continue making progress. Adequate funding is vital for conducting large-scale clinical trials, as well as supporting ongoing research efforts.
2. Ethical Considerations: Research involving live human brain tissue raises ethical considerations, as it necessitates access to patients with varying stages of Alzheimer’s. Balancing the need for research with ethical guidelines is an ongoing challenge.
3. Clinical Trials: The development of promising drugs must pass through rigorous clinical trials. These trials are time-consuming and require a large patient population to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Patient recruitment and retention can be challenging.
RELATED ARTICLE Clinical Trials
Section 7: Promising Directions in Alzheimer’s Research
Despite the challenges, Alzheimer’s research is moving in promising directions. The integration of advanced technologies, collaboration between research institutions, and the pursuit of diverse therapeutic approaches offer hope for further breakthroughs.
1. Advanced Technologies: The use of advanced technologies, such as single-nucleus RNA sequencing, has enabled researchers to gain a deeper understanding of cellular changes in Alzheimer’s. Continued technological advancements will likely drive further discoveries.
2. Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between institutions, researchers, and pharmaceutical companies is essential in accelerating research progress. Sharing data and insights can lead to innovative discoveries.
3. Diverse Therapeutic Approaches: Researchers are exploring diverse therapeutic approaches, from immunotherapies to gene therapies. Diversifying the strategies used to combat Alzheimer’s may lead to more effective treatments.
MORE ARTICLE Sleeping Disorder
Section 8: The Impact on Patients and Families
The breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s research and the development of promising drugs have a profound impact on patients and their families. Improved treatments offer hope for a better quality of life and increased time with loved ones.
1. Enhanced Quality of Life: Promising drugs like donanemab and lecanemab have shown potential in slowing cognitive decline and improving the quality of life for individuals with Alzheimer’s. These advancements can provide relief to patients and their families.
2. Extended Time with Loved Ones: Slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s can mean more time for individuals to spend with their loved ones. Alzheimer’s often takes a toll on family members, and any additional time is invaluable.
3. Reduced Caregiver Burden: Alzheimer’s places a significant burden on caregivers. Improved treatments can reduce the demands placed on caregivers and improve their well-being.
Section 9: The Path Forward
As Alzheimer’s research continues to advance, the path forward holds great promise. It requires sustained funding, ethical considerations, and a commitment to rigorous clinical trials. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies must work together to bring these promising treatments to patients worldwide.
Sustained Funding: Ensuring consistent funding for Alzheimer’s research is vital to maintain momentum and support ongoing breakthroughs.
Ethical Considerations: Researchers must navigate ethical considerations when conducting studies involving live human brain tissue. Balancing the need for research with ethical guidelines is an ongoing challenge.
Commitment to Clinical Trials: The development of promising drugs like donanemab, lecanemab, and remternetug relies on rigorous clinical trials. Patient recruitment and retention must be a priority in these trials to ensure their success.
Global Collaboration: Global collaboration between research institutions, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies is essential in advancing our understanding of Alzheimer’s and accelerating the development of effective treatments.
Conclusion:
Recent discoveries in cellular changes in early Alzheimer’s and the development of promising drugs offer hope in the fight against this debilitating disease. While challenges remain, the dedication of researchers, sustained funding, ethical considerations, and global collaboration provide a path forward towards more effective treatments and, ultimately, a brighter future for individuals living with Alzheimer’s and their families.